[ad_1]
Value Of Items Bought Definition
Value of products offered (COGS) is the price of producing the products offered by an organization. It accounts for the price of supplies and labor immediately associated to that good and for a delegated accounting interval.
As an organization promoting merchandise, you want to know the prices of making these merchandise. That’s the place the price of items offered (COGS) components is available in. Past calculating the prices to provide an excellent, the COGS components also can unveil earnings for an accounting interval, if value modifications are obligatory, or whether or not you want to lower down on manufacturing prices.
Whether or not you fancy your self as a enterprise proprietor or a shopper or each, understanding how one can calculate price of products offered will help you are feeling extra knowledgeable concerning the merchandise you’re buying — or producing.
What Is Value of Items Bought?
Value of products offered is the price of producing the products offered by an organization. It consists of the price of supplies and labor immediately associated to that good. Nonetheless, it excludes oblique bills comparable to distribution and gross sales power prices.
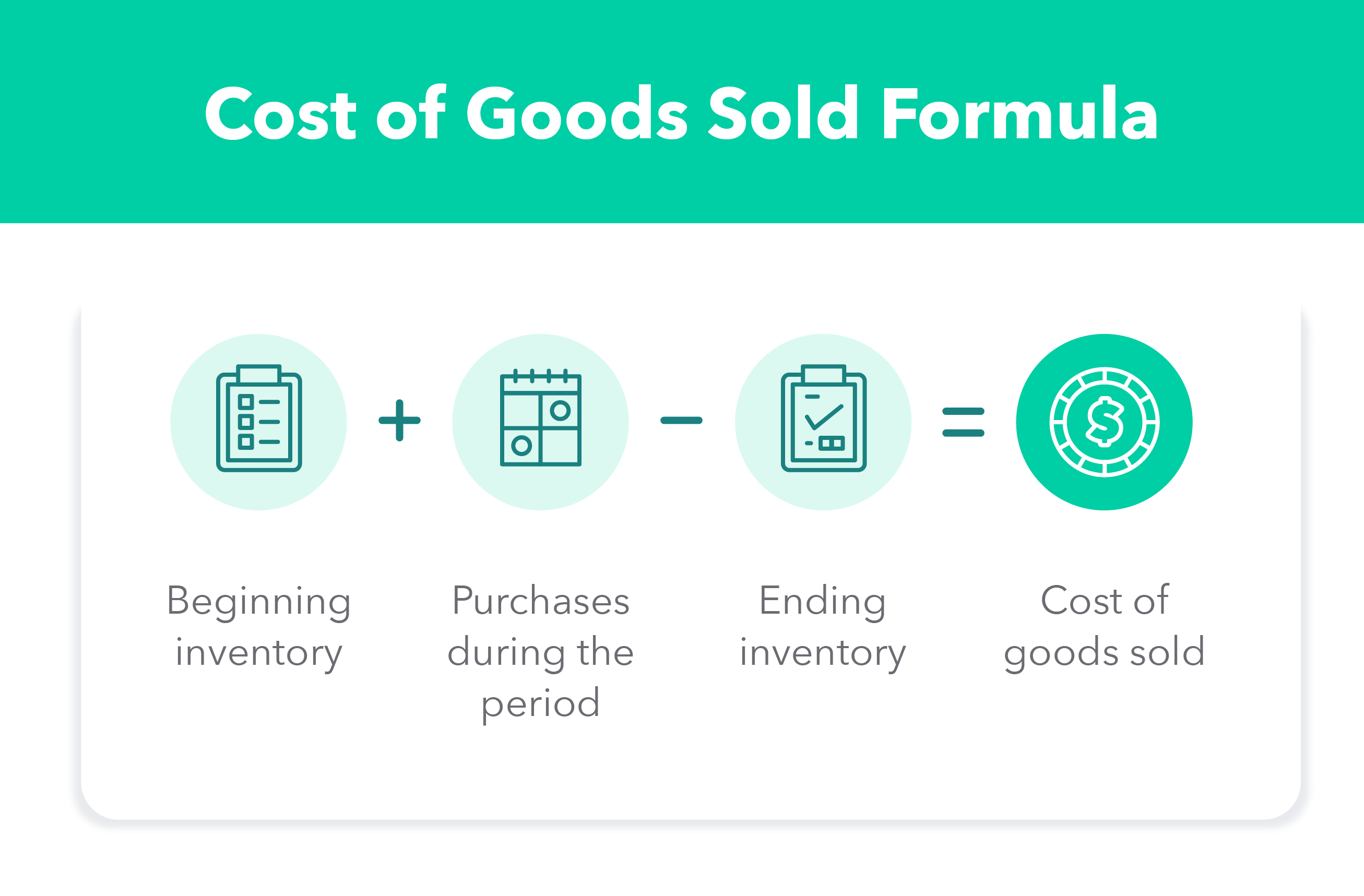
What Is the Value of Items Bought Components?
When promoting a product, you want to perceive the manufacturing prices related to it in a given interval, which may very well be a month, quarter, or 12 months. You are able to do that by utilizing the price of items offered components. It’s a simple calculation that accounts for the start and ending stock, and purchases throughout the accounting interval. Right here is an easy breakdown of the price of items offered components:
| COGS = starting stock + purchases throughout the interval – ending stock |
How Do You Calculate Value of Items Bought?
To calculate price of products offered, it’s a must to decide your starting stock — that means your merchandise, together with uncooked supplies and provides, for example — initially of your accounting interval. Then add within the new stock bought throughout that interval and subtract the ending stock — that means the stock leftover on the finish in your accounting interval. The prolonged COGS components additionally accounts for returns, allowances, reductions, and freight prices, however we’re sticking to the fundamentals on this clarification.
Taking it one step at a time will help you perceive the COGS components and discover the true price behind the products being offered. Right here is the way you do it:
Step 1: Determine Direct and Oblique Prices
Whether or not you manufacture or resell merchandise, the COGS components permits you to deduct the entire prices related to them. Step one is to distinguish the direct prices, that are included within the COGS calculation, from oblique prices, which aren’t.
Direct Prices
Direct prices are the prices tied to the manufacturing or buy of a product. These prices can fluctuate relying on the manufacturing degree. Listed below are some direct prices examples:
- Direct labor
- Direct supplies
- Manufacturing provides
- Gasoline consumption
- Energy consumption
- Manufacturing employees wages
Oblique Prices
Oblique prices transcend prices tied to the manufacturing of a product. They embrace the prices concerned in sustaining and operating the corporate. There could be mounted oblique prices, comparable to lease, and fluctuating prices, comparable to electrical energy. Oblique prices usually are not included within the COGS calculation. Listed below are some examples:
- Utilities
- Advertising campaigns
- Workplace provides
- Accounting and payroll companies
- Insurance coverage prices
- Worker advantages and perks
Step 2: Decide Starting Stock
Now it’s time to find out your starting stock. The start stock would be the quantity of stock leftover from the earlier time interval, which may very well be a month, quarter, or 12 months. Starting stock is your merchandise, together with uncooked supplies, provides, and completed and unfinished merchandise that weren’t offered within the earlier interval.
Understand that your starting stock price for that point interval ought to be precisely the identical because the ending stock from the earlier interval.
Step 3: Tally Up Gadgets Added to Your Stock
After figuring out your starting stock, you additionally should account for any stock purchases all through the interval. It’s essential to maintain monitor of the price of cargo and manufacturing for every product, which provides to the stock prices throughout the interval.
Step 4: Decide Ending Stock
The ending stock is the price of merchandise leftover within the present interval. It may be decided by taking a bodily stock of merchandise or estimating that quantity. The ending stock prices may also be decreased if any stock is broken, out of date, or nugatory.
Step 5: Plug It Into the Value of Items Bought Equation
Now that you’ve all the data to calculate price of products offered, all there’s left to do is plug it into the COGS components.
An Instance of The Value of Items Bought Components
Let’s say you need to calculate the price of items offered in a month-to-month interval. After accounting for the direct prices, you discover out that you’ve a starting stock amounting to $30,000. All through the month, you buy an extra $5,000 price of stock. Lastly, after taking stock of the merchandise you’ve gotten on the finish of the month, you discover that there’s $2,000 price of ending stock.
Utilizing the price of items offered equation, you’ll be able to plug these numbers in as such and uncover your price of products offered is $33,000:
| COGS = starting stock + purchases throughout the interval – ending stock |
| COGS = $30,000 + $5,000 – $2,000 |
Accounting for Value of Items Bought
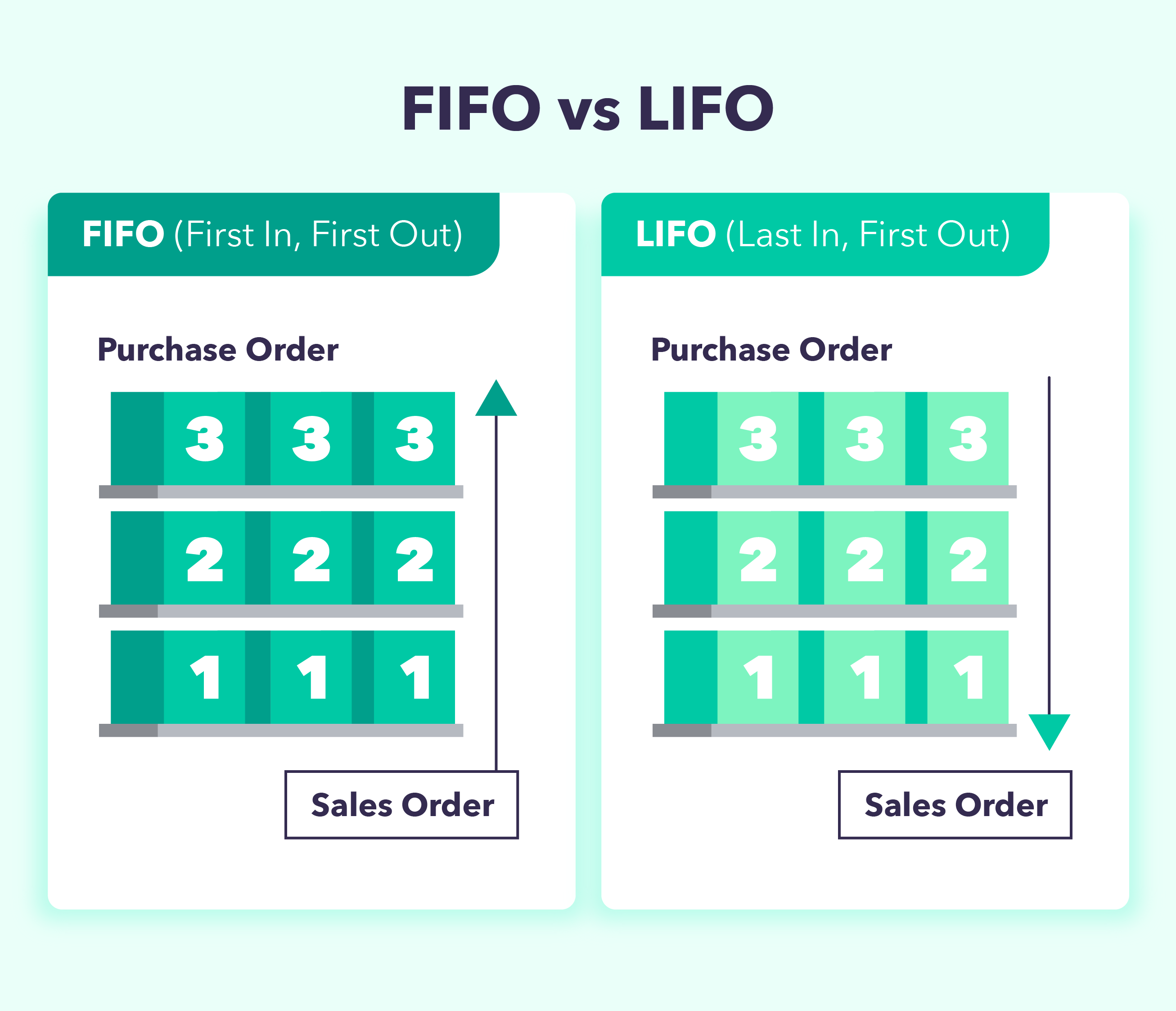
There are totally different accounting strategies used to document the extent of stock throughout an accounting interval. The accounting methodology chosen can affect the worth of the price of items offered. The three primary strategies of accounting for the price of items offered are FIFO, LIFO, and the typical price methodology.
FIFO: First In, First Out
The primary in, first out methodology, also called FIFO, is when the earliest items that had been bought are offered first. Since merchandise costs have a tendency of going up, by utilizing the FIFO methodology, the corporate can be promoting the least costly merchandise first. This interprets right into a decrease COGS in comparison with the LIFO methodology. On this case, the internet earnings will improve over time.
LIFO: Final In, First Out
The final in, first out methodology, also called LIFO, is when the newest items added to the stock are offered first. If there’s an increase in costs, an organization utilizing the LIFO methodology can be primarily promoting the products with the very best price first. This results in a better COGS in comparison with the FIFO methodology. Through the use of this methodology, the online earnings tends to lower over time.
Common Value Technique
The common price methodology is when an organization makes use of the typical value of all items in inventory to calculate the start and ending stock prices. Because of this there will probably be much less of an impression within the COGS by greater prices when buying stock.
Issues for Value of Items Bought
When calculating price of products offered, there are just a few different elements to contemplate.
COGS vs. Working Bills
Enterprise homeowners are probably conversant in the time period “working bills.” Nonetheless, this shouldn’t be confused with the price of items offered. Though they’re each firm expenditures, working bills usually are not immediately tied to the manufacturing of products.
Working bills are oblique prices that maintain an organization up and operating, and may embrace lease, gear, insurance coverage, salaries, advertising and marketing, and workplace provides.
COGS and Stock
The COGS calculation focuses on the stock of your enterprise. Stock could be gadgets bought or made your self, which is why manufacturing prices are solely generally thought-about within the direct prices related along with your COGS.
Value of Income vs. COGS
One other factor to contemplate when calculating COGS is that it’s not the identical as price of income. Value of income takes into consideration among the oblique prices related to gross sales, comparable to advertising and marketing and distribution, whereas COGS doesn’t take any oblique prices into consideration.
Exclusions From COGS Deduction
Since service firms shouldn’t have a listing to promote and COGS accounts for the price of stock, they will’t use COGS as a result of they don’t promote a product — they might as a substitute calculate the price of companies. Examples of service firms are accounting companies, legislation places of work, consultants, and actual property appraisers.
The Backside Line
Working a enterprise requires many transferring components. To make sure an organization is making a revenue and everybody’s paid a good wage, enterprise homeowners ought to have a well-rounded view of the prices related to their items offered. Following this step-by-step information to discover ways to use the price of items offered components is an efficient start line. As all the time, it’s essential to seek the advice of an professional, comparable to an accountant, when doing these calculations to verify every thing is accounted for.
Sources: QuickBooks
Associated
[ad_2]









Leave a Reply